Yellowing of the body
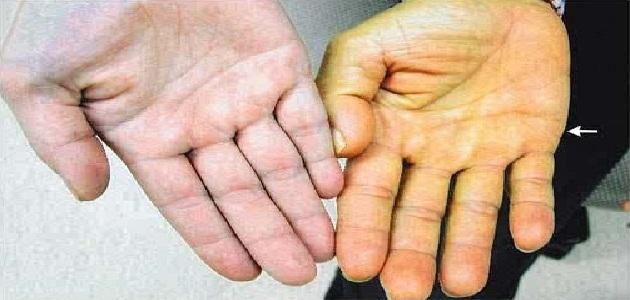
Yellowing of the body, or yellowness, or jaundice, or yellowing, or yellowing of the skin, or yellowness, or jaundice (in English: Jaundice), which is a medical term that describes the change in color of the skin, mucous membranes, and the white part of the eye, due to extremely high levels of bilirubin in the blood and its accumulation. What is known as hyperbilirubinemia in the blood (in English: Hyperbilirubinemia); It is a yellow-brown compound that is formed when old or damaged red blood cells break down. Bilirubin is usually treated chemically in the liver and is then excreted through urine and feces at a normal rate. Either if red blood cells break down at an abnormally high rate or if If the liver is not performing its functions properly, hyperbilirubinemia may occur, and this condition may be an indicator of a medical condition.
Causes of yellowing of the body in adults and its types
As we mentioned, jaundice results from the accumulation of bilirubin in the blood and body tissues. Accordingly, everything that may disrupt the movement of bilirubin from the blood to the liver and then out of the body can cause jaundice. The causes of yellowing of the body in adults are divided based on the factors affecting the exit of bilirubin from the body and their locations. As follows - and will be explained in detail later -:
- Pre-hepatic jaundice: Or pre-hepatic jaundice, which occurs when exposed to a condition or infection that accelerates the breakdown of red blood cells, leading to high levels of bilirubin in the blood and the appearance of symptoms of jaundice.
- Hepatic jaundice: Intra-hepatic jaundice occurs as a result of the liver's ability to process bilirubin being damaged due to it being damaged, either due to infection or exposure to a harmful substance.
- Post-hepatic jaundice: Post-hepatic jaundice occurs due to the inability of the gallbladder to move bile into the digestive system as a result of damage, inflammation, or obstruction to the biliary system.
Pre-hepatic jaundice
Causes of pre-hepatic jaundice include:
Read also:fistula disease- Pseudojaundice: Pseudojaundice is a harmless form of jaundice that usually occurs when eating large amounts of carrots, pumpkin, or cantaloupe. The skin turns yellow due to an excess of beta-carotene and not from an increase in bilirubin.
- Hemolytic anemia: Hemolytic anemia: The production of bilirubin increases as a result of the breakdown of large amounts of red blood cells, as in hemolytic anemia.
- Malaria: Malaria is an infection transmitted by mosquitoes into the bloodstream, and is spread in tropical regions of the world.
- Sickle cell anemia: Sickle cell anemia commonly affects people with dark skin in the Caribbean, Africa and Britain, and is a genetic condition that leads to abnormal growth of red blood cells.
- thalassemia: Thalassemia is a genetic condition similar to sickle cell anemia in that it affects the production of red blood cells. It is common among residents of the Mediterranean and the Middle East, specifically those of South Asian origin.
- Gilbert syndrome: Gilbert's syndrome is a common genetic condition characterized by the accumulation of bilirubin in the blood, which is attributed to the transport of bilirubin from the blood to the liver being too slow.
- Crigler-Najjar syndrome: (in English: Crigler-Najjar syndrome) It is a rare genetic condition that is represented by the absence of an important enzyme that plays a role in helping to remove bilirubin from the blood to the liver.
- Hereditary spherocytosis: Hereditary spherocytosis is an uncommon genetic condition that causes the lifespan of red blood cells to be much shorter than normal.
Hepatic jaundice
Hepatic jaundice occurs if the liver is damaged, and the most prominent causes that cause it are as follows:
Read also:Causes of tiredness and exhaustion- Acute hepatitis: (in English: Acute inflammation of the liver), which may lead to accumulation in the liver due to weakening its ability to conjugate and secrete bilirubin.
- Infectious viral hepatitis: Such as hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C.
- Alcoholic liver disease: (In English: Alcoholic liver disease) where the liver is damaged as a result of alcohol consumption.
- Leptospirosis: Leptospirosis is a bacterial infection spread by animals, especially mice, and is common in tropical regions of the world.
- Glandular fever: Glandular fever, or infectious mononucleosis, is a viral infection caused by the Epstein-Barr virus.
- Misuse of medications: The most prominent causes are the abuse of narcotic substances that give a feeling of high, or the use of pain relievers, specifically paracetamol, in large doses.
- Exposure to substances harmful to the liver: such as phenol; It is a compound used in the plastics industry, and carbon tetrachloride; It is a compound that was used in the past in several processes, such as refrigeration, and is now subject to strict control to reduce its use.
- Autoimmune hepatitis: Autoimmune hepatitis is a rare condition in which the liver is attacked by the immune system. It is the body's natural line of defense against infection and disease.
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis: Primary sclerosing cholangitis is a rare type of liver disease that causes chronic hepatitis.
- Dubin-Johnson syndrome: (in English: Dubin-Johnson syndrome) It is a rare genetic condition in which the liver is unable to conjugate bilirubin with bile in preparation for excretion from the liver.
- Primary gallbladder cirrhosis: Primary biliary cirrhosis is a rare and poorly understood condition that gradually causes liver damage.
- Liver Cancer: Liver cancer is a rare cancer that develops inside the liver and is incurable.
Post-hepatic jaundice
In fact, jaundice may be caused by obstruction or narrowing of the common bile duct, causing bile containing bilirubin to leak into the bloodstream in a condition known as obstructive jaundice or post-hepatic jaundice. Here it must be noted that the bile from all the small bile ducts in the liver flows into another duct, which is the common bile duct. The following are the most prominent cases leading to the occurrence of this type of jaundice:
Read also:Causes of loss of consciousness- Gallstones: (in English: Gallstones) The bile is usually of a liquid nature, but stones may sometimes form in it. Usually, most stones form inside the gallbladder and do not cause any problems, but if the stones exit the gallbladder, they may get stuck in the common bile duct, which prevents the ability to The juice passes from the duct into the intestine and thus leaks into the bloodstream, causing jaundice. However, this is not common.
- Bile duct inflammation: This can prevent the secretion of bile and eliminate bilirubin, causing jaundice.
- Cholestasis: Cholestasis: Cholestasis represents a condition in which the flow of bile from the liver is interrupted, so that this bile, which contains bilirubin, remains in the liver instead of being secreted.
- pancreatitis: Pancreatitis: Pancreatitis can cause the pancreas to enlarge, which may prevent the flow of bile.
- Biliary atresia: Biliary atresia is a condition of unknown cause in which all or part of the bile duct becomes inflamed, which then leads to scarring or fibrosis of the bile ducts, in addition to their narrowing and blockage.
- Gallbladder cancer: Cancer of the gallbladder: Gallbladder cancer may grow to block the common bile duct.
- Pancreas cancer: Pancreatic cancer may occur in the head of the pancreas and may block the flow of bile.
Causes of yellowing of the body in children
Jaundice in children may be a sign of obstruction in the bile ducts, or it may be due to conditions that prevent the liver from properly processing bilirubin. It is necessary to see a doctor if the child shows any signs of jaundice, who will recommend the necessary tests to discover the underlying cause. The cases that may lead to jaundice in children can be discussed as follows:
- Gallstones (in English: Cholelithiasis); These are crystals that accumulate in the gallbladder and block the bile duct.
- Having a bacterial or viral infection that causes damage to liver cells, such as hepatitis A; The most common are hepatitis B and hepatitis C.
- autoimmune hepatitis; It is an immune system disorder that causes immune cells to attack liver cells as if they were an infection.
- Wilson disease (in English: Wilson disease); It is a genetic condition characterized by the accumulation of copper obtained from foods in the liver.
- Cirrhosis of the liver (in English: Cirrhosis); It is a late stage of chronic liver disease in which scar tissue replaces soft, healthy liver tissue.
- Urinary tract infection.
- Underactive thyroid gland (in English: Hypothyroidism).
- Sickle cell anemia.
- Drug toxicity.
- Having infectious diseases that can cause jaundice; Such as typhoid and malaria.
Causes of yellowing of the body in newborns
As we mentioned, jaundice results from the accumulation of bilirubin in the blood, and causes yellowing of the skin and the white part of the eyes. Jaundice is a common condition in newborns, where it is medically called neonatal jaundice. The reason for its prevalence in them is that they have large numbers of red blood cells in their blood, which break down and are destroyed. Replace it frequently, and the newborn’s liver is not fully developed, so it is less effective in removing bilirubin from the blood. Here it must be noted that the placenta undertakes the task of removing bilirubin from the fetus’s blood during pregnancy, and when it is born, the liver takes over this task. Jaundice often goes away spontaneously without causing any harm when the newborn reaches about two weeks of age because his liver is more effective in processing bilirubin. The causes of high bilirubin in newborns can be mentioned as follows:
- Physiological jaundice: This type of jaundice is considered normal; It occurs in response to the newborn's decreased ability to remove bilirubin; The newborn cannot get rid of bilirubin during the first few days of birth, and it is often difficult at first to know whether jaundice is caused by another problem.
- Jaundice associated with breastfeeding failure: Some newborns who are not breastfed well may suffer from dehydration due to malnutrition, and this also causes decreased urination of the newborn, which leads to the accumulation of bilirubin in the body, causing jaundice.
- Breast milk jaundice: It affects newborns during the first week and reaches its peak in the second week of the child’s life. It can last from three weeks to 12 weeks. The cause of this jaundice may be due to the presence of a substance in the mother’s milk that may work to increase the amount of bilirubin that the child’s body can reabsorb. This is not considered This type is dangerous but requires testing for other problems that may be serious.
- Rhesus disease: (in English: Rh disease) It is a hemolytic disease that may affect newborns due to their blood type being different from the mother’s blood type.