Treatment of uterine fibroids
There is no single ideal way to treat all cases of uterine fibroid (uterine fibroid). Rather, the doctor determines the appropriate treatment from among the many available treatment methods based on several factors: Such as the symptoms appearing on the affected woman, the severity of these symptoms, in addition to the location of the fibroids, and the following is a statement of the therapeutic methods in some detail:
Wait and watch
The principle of watchful waiting depends on following up and monitoring fibroids. This is in the case of uterine fibrosis that is not accompanied by any symptoms; In this case, uterine fibroids do not require treatment. This procedure may also be used if there are minor symptoms that do not cause major discomfort. Fibroids rarely affect pregnancy and are not considered cancerous. It grows slowly or may not grow at all, and tends to shrink after menopause due to low levels of reproductive hormones. Through this procedure, the woman is monitored, followed up, and tests are performed periodically and regularly, every 6-12 months. To determine whether the fibrosis is changing in size, and whether the woman is planning to become pregnant, in addition to tracking the accompanying symptoms and the extent of their worsening.
pharmaceutical
Medications are the first treatment method that a doctor may resort to to treat uterine fibroids, and although fibroids cannot be removed using medications; However, it may be able to shrink these tumors, and its working principle depends on targeting the hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle, and thus it treats the symptoms associated with uterine fibroids, such as: heavy usual monthly bleeding, and pressure in the pelvic area, and it is worth mentioning that pain-relieving medications can be taken. ; Such as ibuprofen to relieve pain, with the need to consult a doctor and adhere to the instructions attached to the medication to avoid incorrect use of it. There are also many other medication options that the doctor may prescribe if the need arises, including the following:
Read also:What are the symptoms of egg fertilization?- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists: Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists rely on the principle of their work to put the body in a temporary state similar to menopause, by preventing the body from producing both the hormones estrogen and progesterone. Which causes the menstrual cycle to stop, and also shrinks the fibroids. It also often contributes to improving the condition of anemia. Accordingly, the doctor may sometimes prescribe it before resorting to surgery to reduce the risk of bleeding, but it is worth mentioning that when stopping taking medications this group; The fibroid usually returns to its previous size, and since these medications are also associated with many side effects; They are only used for a short period of time, less than six months. Examples include: Leuprolide, Goserelin, and Triptorelin.
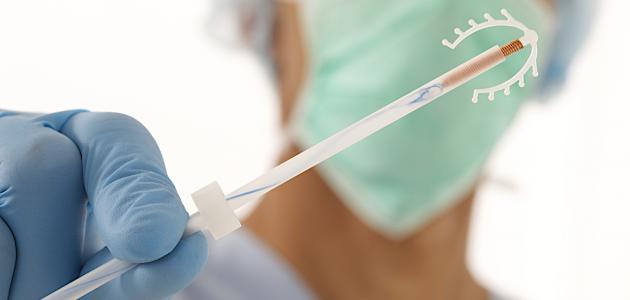
- Hormonal IUD: (in English: Hormonal intrauterine device), which is a small T-shaped plastic device that is placed inside the uterus; To slowly secrete the synthetic progesterone hormone known as Levonorgestrel, which is indicated to prevent pregnancy and only alleviates the symptoms associated with uterine fibroids; The monthly bleeding is less heavy than before, and this is due to the decrease in the thickness of the uterine lining due to the mechanism of action of the drug, which is to stop the growth of the uterine lining quickly, but it does not eliminate fibroids or reduce their size.
- Tranexamic acid: (in English: Tranexamic Acid), which is a non-hormonal medication that can be prescribed by a doctor in cases where the use of a hormonal IUD is not appropriate. Such as not wanting to use contraceptives; It is noteworthy that pills containing tranexamic acid are not considered contraceptives and do not affect the chances of pregnancy. The mechanism of action of tranexamic acid is to stop the bleeding of small blood vessels in the lining of the uterus, which reduces blood loss by approximately 50%, and thus reduces heavy bleeding. Menstrual bleeding. Taking it is limited to days when heavy menstrual bleeding occurs.
- Selective estrogen receptor modulators: (in English: Selective estrogen receptor modulators) and SERMs for short; Although the mechanism of action of this group of drugs is not yet confirmed; However, it affects estrogen levels, so it may be able to reduce the size of fibroids without causing menopausal symptoms.
- Other medicines: The doctor may prescribe other types of medications, such as: oral contraceptives, which may help control menstrual bleeding; But it does not shrink fibroids.
Read also:Does having an ovarian cyst prevent pregnancy?
Non-invasive procedures
MRI-guided focused ultrasound surgery is a therapeutic procedure for uterine fibroids, which can be used while preserving the uterus. It does not involve making surgical incisions to get rid of fibroids; Rather, this procedure involves inserting the patient into an MRI scanner supported by a high-energy ultrasound transducer. Through the images generated by the device, the doctor can determine the exact location of the fibroid, and then the transducer is focused on it. In turn, the ultrasound waves heat small areas of fibrotic tissue and destroy them. In fact, this procedure does not require hospitalization. It can be performed in outpatient clinics, and it is considered a modern technique whose long-term safety and effectiveness are still under research, but it has so far been shown to be an effective and safe technique.
Minimally invasive procedures
Some minimally invasive surgical procedures can destroy uterine fibroids without actually removing them with surgery; However, this type of procedure, which does not involve removing the uterus, may involve the risk of the growth of a new fibroid and causing the symptoms that accompany it. Among the minimally invasive procedures are the following:
- Embolization of uterine fibroids: (in English: Uterine fibroid embolization) UFE for short, or what is also known as uterine artery embolization; This type of minimally invasive procedure uses fluoroscopy, which is a type of X-ray, through which certain agents and molecules are directed to the uterus and uterine fibers to block the arteries that feed these tumors. Which causes it to shrink and reduce its size.
- 'Radiofrequency ablation: (in English: Radiofrequency ablation); This procedure relies on the use of heat generated by radiofrequency to reduce the size of uterine fibroids without the need for a hysterectomy. However, it does not remove fibroids, which means that they may grow again after the operation or new fibroids may appear. In the context of the conversation, it is worth noting that it is preferable to perform this type of procedure for women who do not suffer from very large fibroids, and who have not previously undergone complex surgeries in the abdominal area. Their uterus is located under the belly button. It is also indicated that it can be performed in outpatient clinics, and the person concerned can leave the hospital on the same day.
- Hysteroscopic myomectomy: (in English: Hysteroscopic myomectomy); This procedure may be an option when fibroids are inside the uterus, specifically under the lining of the uterus, known as submucosal uterine fibroids. During this procedure, tools are inserted through the vagina and cervix to the uterus to remove these tumors.
- Robotic myomectomy: (in English: Robotic myomectomy); It is a type of laparoscopic myomectomy. In this minimally invasive procedure, fibroids are removed without affecting the uterus. This procedure is characterized by less blood loss, fewer complications, and a shorter period of stay in the hospital, in addition to a faster return to performing daily activities compared to open abdominal surgery. Although this procedure is safe and effective; However, it is not suitable for all women with uterine fibroids, and therefore it is always worth consulting a doctor to learn about the available treatment methods in addition to their benefits and risks.
- Endometrial ablation: (in English: Endometrial ablation); Endometrial ablation is a minimally invasive procedure in which a specialized instrument equipped with heat, microwave energy, hot water, or electrical current is inserted into the uterus; To destroy the lining of the uterus, which either stops or ends the menstrual cycle or reduces its flow. Which effectively controls abnormal bleeding associated with uterine fibroids. It is also noted that although submucosal fibroids can be removed during a hysteroscopy procedure to remove the lining of the uterus, fibroids located outside the inner lining of the uterus cannot be removed by relying on this procedure.
Read also:What is menstruation?
Traditional surgical procedures
Traditional surgical procedures are one of the treatment options that can be used, the most prominent of which are the following:
- Transabdominal myomectomy: (in English: Abdominal Myomectomy), which is a major surgical procedure that involves the patient undergoing general anesthesia and making an incision through the skin into the uterus in the lower abdomen, then removing fibroids from the uterine wall, and finally suturing the uterine muscles using several layers of stitches. It is preferable to resort to this Surgical operations in the event of large or many fibroids growing in the uterine wall.
- Hysterectomy: (in English: Hysterectomy); It is a major surgical procedure that some women may prefer to solve the problem of fibroid tumor and its accompanying symptoms once and for all. It is recommended to perform this type of surgical procedure for women who suffer from large fibroid tumors, or severe bleeding, and at the same time do not want to have more children. It stops menstrual bleeding, relieves pressure in the pelvic area, and reduces the frequent need to urinate, in addition to ensuring that fibroids do not grow again after hysterectomy.
Shredding during fibroid removal
During the fibroid removal process, a special medical device is used to cut the uterine tissue or fibroid into small pieces electrically or mechanically to facilitate their removal laparoscopically, or through the vagina, or through small abdominal incisions that may be made. This process is known as morcellation. It is usually only resorted to in the event of undergoing the following surgical operations:
- Complete or total laparoscopic hysterectomy and the uterus is too large to be removed vaginally.
- Partial laparoscopic hysterectomy. This type of hysterectomy means that the cervix remains in place.
- Laparoscopic myomectomy.
Reasons to see a doctor
You should see a doctor if any of the following symptoms appear:
- Feeling constant and persistent pain in the pelvic area.
- Spotting or bleeding between periods.
- Difficulty emptying the bladder of urine
- Menstrual bleeding is very heavy, prolonged, or accompanied by pain.
- Low red blood cell count for no known reason; Which causes anemia.