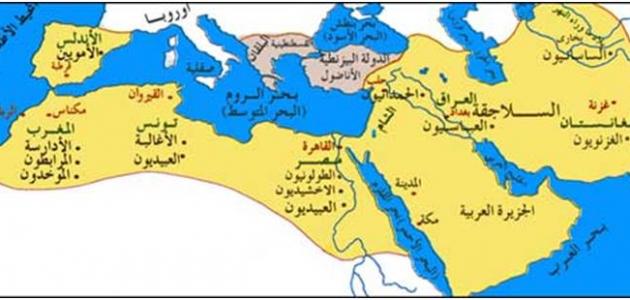
borders of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire appeared at the end of the Middle Ages on the borders of the Islamic world with Europe. It rose and expanded in Asia Minor to become a great power among the powers that existed at the time, and the Ottoman Empire became of great value among the balance of major powers. Then it spread to southern Europe and the ancient Near East, and in the middle of the fifteenth century AD, the Ottoman Empire had extended to include several regions of the Balkans and Greece, and during the period 1516-1517 AD the Ottoman Empire controlled Syria, Egypt and Palestine, in addition to controlling most of the lands of Hungary in the year 1526 AD , then Iraq in the year 1530 AD, and the Ottoman Empire reached its maximum extent by the middle of the sixteenth century AD, so the Ottomans took control of the Arabian Peninsula, most of the countries of North Africa, in addition to many islands in the Mediterranean Sea, and the Ottoman expansion began to stop in 1683 AD when He failed to capture Vienna, and the Ottomans lost Budapest three years later.
Then the Ottoman Empire began to weaken in conjunction with the expansion of Russia in the north, the emergence of the Safavid state, which was in complete hostility with the Ottoman Empire, and the emergence of other countries on the scene such as Portugal, Spain, England and France, who quarreled with the Ottoman Empire by seizing some of the Ottoman lands and many parts of the world. The Islamic caliphate fell and ended completely with the occurrence of the First World War, which resulted in the independence of the countries that were affiliated with it. In this article, we will talk briefly about the stages of the expansion of the Ottoman state.
Read also:Where is Puppet Hill located in Istanbul?The emergence of the Ottoman Empire and its history
The Ottomans are a group of Turkish tribes.[XNUMX] Their origin goes back to their supreme grandfather, Suleiman Shah, who belongs to the Qabi Alp clan, and after the death of Suleiman Shah, his family was divided into two parts. The plains of Scott from western Anatolia, and the eastern slopes of the Tomatj Mountains located on the borders of the Byzantine state as a reward for him, and in the year 1288 AD Ertugrul died and his son Othman took over the leadership after him. Beck and giving him all the lands and castles that he was able to seize, and gave him many privileges, including that he was allowed to mint the currency in his name as he mentioned his name and his achievements in the Friday sermon.
After the death of Sultan Alaeddin, the heads of the tribes met and agreed to grant Othman the caliphate, as Othman fortified his city and expanded his empire gradually, starting from the city of Nicaea to reach the Byzantine lands in Anatolia, and from the confrontations of Othman with the Byzantines, a battle took place in the year 1301 AD in the Qureen Hisar region, which resulted in About the fall of the Byzantines and the victory of the Ottomans and their control over many regions, and among the cities that Osman controlled was Bursa in 1329 AD, and the city of Nicaea in 1331 AD, then he controlled the city of Nicomedia in 1337 AD, as for the actual founder of the Ottoman Empire who enacted laws and laid down the constitution and systems of the state On the various political, administrative and economic levels, and the division of powers in it is Sultan Orhan, who ruled in the period 1326-1359 AD.
Read also:Where is Mecca located?The sultans followed successively over the Ottoman Empire, when Sultan Murad I assumed power, the Ottomans had settled, taking the Gallioli fortress as a headquarters for their war operations, and Sultan Murad I took control of the Balkans, Thrace, and Macedonia, and Edirne became the capital of the Ottoman Empire, and in 1389 AD the famous battle of Qusuh took place, after which it expanded The borders of the Ottoman Empire to include Ankara and other large lands, but when Bayezid I assumed power, he deliberately established his bases in Anatolia and the Balkans, but he was defeated by Tamerlane in the Battle of Ankara, and this defeat was in 1402 AD and resulted in Bayezid I falling captive in the hands of Tamerlane, and as a result he occupied Tamerlane, the Asian part of the Ottoman Empire, then Sultan Mehmed I took power, and his son Murad II succeeded him, who succeeded in restoring the Ottoman Empire to what it was, and continued his war against Europe, and he followed his reign after Sultan Mehmed II, who bears the title of Mehmed the Conqueror, to reach the state The Ottoman Empire was the height of its prosperity, and the Byzantine state was eliminated forever. During his reign, Constantinople was conquered in 1435 AD.
Extension of the Ottoman Empire in the Arab world
During the reign of Sultan Selim I in the period 1512-1520 AD, the Ottoman Empire turned to the Arab world after it stopped moving towards Europe, and many disputes occurred between the Mamluks and the Ottomans to seize the border emirates, especially the Emirate of Dhul Qadr, and the disputes ended with the Mamluks and Safavids controlling it and defeating the Ottomans.
Read also:Where is Andalusia located and what are its borders?Ottoman control of the Levant
The Mamluk state extracted power from the Ayyubids in the thirteenth century and ruled the Levant, Egypt, Yemen, and the Hijaz. Which led to his dissatisfaction, and the state's administrative and military systems retreated, at a time when the military and administrative systems of the Ottomans developed, and the confrontation took place in Syria near Aleppo between the Ottoman state led by Selim I, and the Mamluk state led by Qansuh al-Ghuri, in the battle of Marj Dabiq in 1516 AD The Ottomans were victorious, and Qansuh was killed, and the Mamluk forces withdrew thereby from Syria to Egypt, and the influence of the Ottoman Empire extended over the southern part of Syria, and the Levant was divided into two parts: the northern part of Damascus under the administration of the ruler of Aleppo, and the southern part under the administration of the ruler of Damascus.
Ottoman control of Egypt, Hijaz and Yemen
As for the control of the Ottomans over Egypt, Yemen, and the Hijaz, Sultan Selim I offered the new Mamluk ruler Tuman Bey, who was elected in Egypt, to remain the ruler of Egypt in return for submitting to and recognizing the control of the Ottoman state, but he refused, and the Mamluks rose again to confront the Ottomans. However, they failed, as the Ottomans took control of the city of Gaza, and reached the Delta, then a major confrontation occurred between the two parties on the outskirts of Cairo in the year 1517 AD, which led to the victory of the Ottomans over the Mamluks, and their entry into Egypt, to announce the end of the Mamluk state, whose rule lasted from 1250 AD to 1517 AD, As for the Hijaz, it was subjected to the Ottoman Empire after the Sheriff of Mecca, Zain al-Din Barakat, declared his loyalty to the Ottoman Sultan Selim I, who granted him security, and handed him the keys of the Holy Kaaba, to officially declare Sultan Selim I the Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques.
As for Yemen, the Ottoman Empire extended to it through the arrival of a Yemeni delegation to Cairo after the Ottomans took control of it to offer allegiance to Sultan Selim I, and the Ottomans relied on Yemen's strategic location to protect the holy places in the Hijaz, and to control the Red Sea and the Arabian Sea. Suleiman Pasha campaign aimed at annexing Yemen to it before the Portuguese preceded them, and thus the Ottoman Empire took control of Yemen by annexing Aden, and closing the Bab al-Mandab Strait; To prevent the arrival of foreign fleets to Yemen.
Ottoman control of Iraq
In the year 1534 A.D., Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent led his campaign against Baghdad, which was ruled by the Safavid state since the sixteenth century. Sultan Selim I controlled the northern region of Iraq, which made Suleiman the Magnificent plan to invade the Safavids, and thus waged the war against Persia, and defeated them to reach Tabriz, the capital of the Safavid state, and entered it without resistance from its people, then Suleiman the Magnificent advanced to Iran, and from there he headed to Baghdad, and entered it without a fight because its Persian ruler fled from it, and then the clan sheikh presented his allegiance to the Sultan, who kept him as governor of Basra receiving his orders from him, and the Ottomans annexed Basra officially and continued their march towards the northern shores of the Arabian Gulf, and Iraq developed during the reign of Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent, where he carried out major reforms in agriculture and irrigation, established schools, and deliberately applied a feudal military system, and Iraq became, during his reign, divided into five states: Baghdad, Mosul, and Basra Al-Ahsa, and Shahruz.
Ottoman conquests in Europe
Europe has fought many wars against Muslims since ancient times, as the Roman state tried to eliminate the Islamic state, and the Crusades passed through the Arab East, ending with the fall of Andalusia at the hands of the Spaniards, but the Muslims defeated them in more than one era, including when the Ottoman state emerged and triumphed over Europe in what remained of Asia, as the Serbs and Bulgarians joined the Ottoman Empire, then its borders extended to the Danube River.
At the same time that the Ottomans were preoccupied with annexing eastern Europe, as the other Ottoman armies were able to control the rest of the small emirates in Anatolia that remained from the Seljuk era, however, the European powers dared after a while to confront the Ottoman Empire and it was headed by the King of Hungary, as Timur was also preparing To confront the Ottomans, and thus the European powers had gathered from the East and Morocco to fight the Ottoman Empire, and as a result of the meeting of the countries of Europe the mobilization of 120,000 soldiers near the Danube River in Bulgaria, but Sultan Bayezid I defeated them in a crushing defeat, and their leaders fell prisoners in his hands, and as a result the state expanded The Ottoman Empire from the Euphrates River in the east to the Danube River in the west, then the Ottomans besieged Constantinople until it fell into their hands, but the events reversed when Timur, the Mongols, raided them from the east, which forced Sultan Bayezid I to complete the peace contract with its people, on the condition that they commit to paying tribute and building a mosque for the Muslims. In which.
Timur ruled the Tatars in Central Asia, and in Persia, and expanded his kingdom to include the countries of Afghanistan, India, Georgia, Kurdistan, and Armenia, and reached Aleppo, Damascus, and the plains of Ankara, and there he confronted Sultan Bayezid, but the Tatar attack defeated him after fierce fighting and courage Kabir, until he fell captive, died, and was buried next to his father, after which the Ottomans lost most of their military power, and here the Ottoman expansion had stopped, and the Ottomans absorbed their defeat and began to build their strength again, and when Timur died, Sultan Muhammad I bin Bayazid was able to overcome various obstacles He regained everything lost by the Ottomans, took control of Bulgaria and Serbia again, and Edirne became the capital of the Ottoman Empire. After him, his son Murad II continued the unification of the Ottoman Empire, and built a strong army and economy. During the reign of Sultan Mehmed II, Constantinople was conquered in 1453 AD, and he was named after Muhammad the Conqueror.