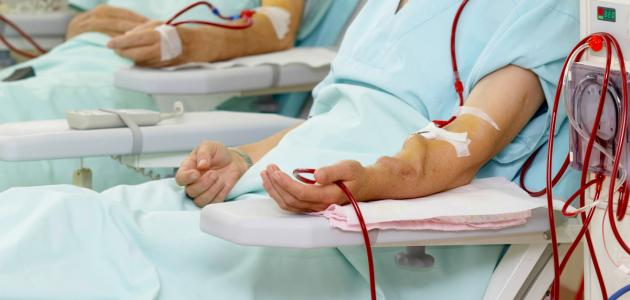
Reasons for dialysis
Kidney dialysis, also known as dialysis, or membrane dilysis, is a treatment option that compensates for some of the deficiencies in kidney function. It is resorted to when the kidneys lose their ability to meet the body’s needs and perform their functions completely. Specifically, it is resorted to It occurs when the kidneys lose approximately 85-90% of their functions, and the glomerular filtration rate (*) is less than 15 milliliters per minute.
In fact, the decision to start dialysis depends on the patient’s age, general health, laboratory test results, the patient’s readiness to begin treatment, the severity of the symptoms that appear related to kidney failure, in addition to the emergence of some other problems in the body, such as: the occurrence of nutritional problems. And fluid balance, and the inability to control blood pressure. It should be noted that in some cases dialysis is started before these problems appear. In any case, determining the appropriate time to start dialysis depends largely on the decision taken by the specialist doctor and the person concerned. If the doctor decides that the patient needs dialysis; The patient must adhere to all sessions and not skip any of them, in order to avoid complications that may result from untreated kidney failure. Below is a description of the most common cases that may require dialysis.
Read also:Conditions for kidney donation
Chronic kidney failure
Chronic renal failure (in English: Chronic renal failure), or CRF for short, is damage to the kidneys and their inability to fully perform their functions. This damage occurs gradually over a long period of time, and diagnosing kidney failure early plays an important role in treating the condition. Reducing the chance of complications arising. Treatment of chronic kidney failure depends on treating the cause. In general, treatment aims to slow down the speed of the disease’s progression. It is worth knowing that chronic kidney failure cannot be eliminated except through dialysis or a kidney transplant. It is worth noting that chronic kidney failure may not be accompanied by the appearance of any significant symptoms or signs, because the kidneys have a great ability to perform their functions in their weakest states. Chronic kidney failure may be diagnosed through laboratory tests conducted on blood and urine samples only, without... Feeling any symptoms. On the other hand, advanced cases of kidney failure may cause swelling in the body known as edema as a result of the kidneys’ inability to get rid of excess fluids and salts. Edema appears in the case of chronic kidney failure in the feet or ankles. Or the legs, and in a few cases it may appear in the hands or face. Other symptoms that may accompany chronic kidney failure include: chest pain, fatigue, headache, muscle pain, nausea, and shortness of breath.
Read also:What are the harms of holding urine?Suffering from chronic kidney failure is often attributed to one of the diseases that accompanies the sufferer for a long period of time. It is worth noting that these diseases do not often cause kidney failure in the initial stages. Among these diseases and problems are the following:
- High blood pressure, because high blood pressure in the long term may damage the glomeruli of the kidneys, which are the part responsible for filtering waste in order to get rid of them.
- Conditions that cause long-term obstruction in the urinary tract, such as: kidney stones, enlarged prostate, and some types of cancer.
- Type 1 and 2 diabetes. It has been shown that there is a link or relationship between uncontrolled diabetes in its advanced stages and kidney failure. It is worth noting that kidney failure does not usually occur during the first ten years of diabetes.
- Vesicoureteral reflux: This condition is represented by the reflux of urine into the kidneys instead of being excreted outside the body.
- Interstitial nephritis is defined as a kidney disorder in which the spaces between the kidney tubules become enlarged, and this in turn may cause problems in the kidneys.
- Polycystic kidney disease is a hereditary disorder in which a group of cysts develop primarily on the kidneys, leading to the kidney losing the ability to perform its functions, in addition to increasing its size beyond the normal limit. Most often, these cysts are benign and not normal. Cancerous.
- Glomerulonephritis: As we mentioned, the glomeruli are the part responsible for filtering waste and ridding the body of them in the form of urine. These glomeruli may become inflamed suddenly or gradually.
- Pyelonephritis is a type of urinary tract infection in which one or both kidneys are affected, as a result of a bacterial or viral infection. In a few cases, this type of infection can cause kidney failure, especially if it occurs repeatedly.
- Other causes: In addition to the above, chronic kidney failure can result from other conditions, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (*), taking some medications for a long period of time, and addiction to legally prohibited substances such as heroin, malaria, and others.
Read also:What are the harms of holding urine?
Acute renal failure
Acute kidney injury is defined as a health condition that affects the kidneys suddenly and within a very short period of time, usually two days or less. The severity of this injury ranges from a slight loss of kidney function to complete kidney failure, and it is worth noting. Acute kidney failure is a health condition that can be cured if it is detected and treated early. It is worth noting the need to treat this condition in a timely manner. In fact, the treatment and duration of acute kidney failure depends on identifying the disease or problem that caused it and the speed of the kidney’s recovery and response. Most Cases require admission to the hospital to receive treatment, and the treatment options available in cases of acute renal failure include the following:
- Treating the cause: The underlying cause of acute kidney failure must be treated to get rid of the problem.
- Treatment of complications: A specialist doctor should treat the complications that accompany acute renal failure according to their nature, including the following:
- Achieving a balance in the level of fluids in the body, as excess fluids are eliminated through diuretics, while the patient is provided with fluids intravenously if he suffers from dehydration.
- Balancing the level of electrolytes in the body by giving appropriate medications.
- Hemodialysis: Hemodialysis is usually used in such cases, and its use aims to rid the body of excess fluids and toxins.
In the context of talking about acute renal failure, it is worth clarifying that the cause of acute renal failure is due to the lack of blood flowing in the kidneys, or due to obstruction of the ureters (*), or the occurrence of some problem in them, or exposure to a direct injury, and the elderly who are over the age of 65 years are considered People with chronic diseases such as: chronic kidney failure, diabetes, liver disease, and heart failure are among the groups at risk of developing acute kidney failure. It is worth noting that the symptoms accompanying this condition vary depending on the cause, and there are many cases that are not accompanied by the appearance of any symptoms and are It is discovered through laboratory examinations and analyses, and among the symptoms that may appear in a person with acute renal failure are the following:
- Swelling of the legs, ankles, and around the eyes.
- Excretion of small amounts of urine.
- shortness of breath.
- Fatigue and tiredness.
- confusion.
- nausea;
- Feeling pain in the chest area.
- Coma and seizures in severe cases.
other reasons
There are many other reasons that require dialysis, including:
- Hyperkalemia in the blood: Hyperkalemia is considered a critical condition that requires medical monitoring. Hemodialysis is used to treat hyperkalemia in cases where the patient does not respond to other treatments, or in cases where he suffers from complete kidney failure.
- Kidney injury: Kidney injuries are divided into two types: bruises and penetrating injuries. The first type may not be detected except through laboratory tests or through the appearance of bruises as the only external sign. As for injuries that penetrate the skin, they usually result from stab wounds with a knife or other sharp objects, and the kidneys may be harmed. Without the site of the wound being close to it, and in severe cases of kidney injuries in general, dialysis may be the appropriate treatment option.
The importance of adhering to dialysis sessions
People undergoing dialysis sessions should commit to attending all treatment sessions, as not attending one treatment session repeatedly will harm the patient’s health. This confirms that the patient is not receiving treatment as required, because this provides the opportunity for toxins to rise in their levels in the body. As for For not attending a single treatment session while attending the rest of the sessions; It is difficult to predict how the body will respond to not attending that session. In some cases, the body is able to deal with the problem for a short period of time, while the bodies of some sufferers cannot deal with it. Hence, we call on the necessity of committing to all dialysis sessions and discussing the matter with the doctor in the event of any emergency that prevents the ability to attend a session. Hemodialysis.
Medical care for dialysis cases
In fact, dialysis requires a joint effort from the patient, his family, and medical care providers, and we explain the role of each individual medical care provider when performing dialysis:
- the doctor: The nephrologist provides medical care first by prescribing dialysis to the patient, and then following up on the health of the affected person, including the complications that may appear. That is, he follows up on the patient’s health condition before and after starting treatment.
- Pathogen: The nurse is responsible for following up with the patient; This is done by ensuring that he receives medications and treatments in the required manner, supervising the dialysis process, and supervising the health care programs through which both patients and their families are trained in home dialysis procedures.
- Social worker: The social worker provides counseling to help patients and their families cope with kidney disease and the changes that occur to the patient's life at home and the workplace, that is, he helps the patient and his family improve the quality of life.
- Nutritionist: The nutritionist recommends a diet that suits the patient's health condition, as the patient's nutrition before and after dialysis is an important part of the treatment plan.
Margins:
(*) Renal filtration rate: Renal filtration is defined as an examination performed to verify the health of the kidneys, as it determines the amount of blood that passes through the renal glomeruli per minute. The glomeruli are defined as the small filters in the kidneys that filter waste from the blood.
(*) Lupus erythematosus: It is the most famous type of lupus, in which the immune system mistakenly attacks some organs and tissues of the body. The parts that may be affected include the joints, skin, brain, kidneys, and blood vessels.
(*) The ureters: They are two thin tubes responsible for transporting urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder, and they are considered one of the parts of the urinary system.