Kidney transplant
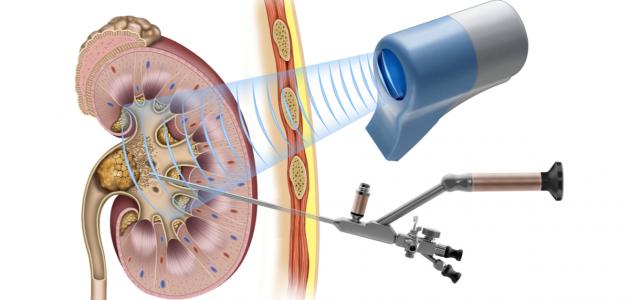
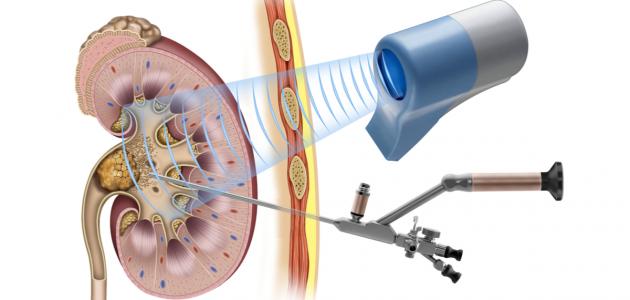
Kidney Transplant is defined as a surgical operation that aims to place a new kidney from a living or deceased donor to a person whose kidneys are no longer able to perform their functions. The patient undergoes the operation under general anesthesia, and this surgical operation lasts 3-4 hours. During which the doctor places the donated kidney in the lower abdomen, near the thigh, and a kidney transplant is chosen for those suffering from the last stages of kidney failure (in English: End-Stage Renal Disease); This is because it provides a better quality of life for the patient instead of permanent dialysis of the kidneys, as the probability of the patient’s death becomes less, and it is also less expensive than the patient having to undergo dialysis throughout his life. It should be noted that there are many conditions for a kidney transplant; As it may not be suitable for all patients.
Conditions for kidney donation
The medical team usually conducts evaluation tests before performing the operation. This is to determine the suitability of the kidney that will be transplanted to the patient, in terms of blood and tissue type, and everyone must perform these tests, regardless of the type of donor or his relationship to the patient. The following is a statement of the most prominent criteria that are evaluated to determine the possibility of performing the operation:
- Blood type: (English: Blood Type) There are four main types of blood: A, B, AB, and O. The recipient’s blood and the donor’s blood must be of the same blood type or their types must be compatible, as follows:
- Type A blood corresponds to either type A or O blood.
- Blood type B corresponds to blood types B or O.
- Type AB blood is compatible with all types A, B, O, and AB blood; It is called the Universal Recipient.
- Blood type O is compatible with blood type O only, and although a patient with type O blood can only receive a kidney from a donor of the same blood type, he is called a universal donor (in English: Universal Donor) because he can donate to all blood types.
- Fabric type: Or examining the human leukocyte antigens present in the body’s cells. This examination evaluates the possibility of the donated kidney functioning for a long time, and the possibility of the body rejecting it. Through the genetic markers present in it.
- Compatibility: (in English: Crossmatch) The immune system produces antibodies (in English: Antibodies) to fight foreign bodies that enter the body: such as bacteria and viruses, and the compatibility test evaluates the possibility of the recipient’s immune system recognizing the donor’s kidney as a foreign body. By mixing a blood sample from the donor with a blood sample from the infected person and observing whether the antibodies from the infected person’s body will fight the antibodies present in the donor’s body. This is because the recipient's body will destroy the donor's kidney after a kidney transplant if there are antibodies to the donated kidney.
Read also:What are the harms of holding urine?
Donor conditions
In fact, in addition to deceased people, healthy and living people can donate many organs, such as a kidney or part of an organ: such as the lung, liver, and pancreas. The surgeon usually takes the kidney from the donor in two ways: either through an open surgical procedure during which he makes a wound. Its length is approximately 20 cm, or by performing the operation laparoscopically (in English: Laparoscopic Surgery) by inserting thin tubes through four small wounds whose length does not exceed ten centimeters, after which the donor can leave the hospital after the operation within 2-4 days. In addition to the tests and evaluations mentioned previously, there are some conditions for people to be able to donate a kidney, and the following is a description of some of them:
- The donor’s consent to donate his kidney must be voluntary.
- The donor's kidney function must be normal.
- The person must be healthy, physically and mentally.
- The donor must be over 18 years old.
- The body mass index must be less than 35 kg/mXNUMX.
- The donor must not suffer from high blood pressure, diabetes, cancer, hepatitis, or any organic or infectious diseases.
Recipient terms
People with end-stage kidney failure are usually candidates for a kidney transplant; In this case, the kidneys lose their ability to filter and purify the body of toxins, which leads to their accumulation in the body. However, there are some cases that may prevent the operation for affected people, and the following is a statement of some of the most important of them:
Read also:Reasons for urinating frequently- old age; As people older than 60 years of age undergo a complete cardiac and physical evaluation before their eligibility for the operation is determined.
- Having recently had a heart attack or suffering from severe heart disease.
- Current or previous cancer.
- Having a mental disorder.
- Dementia.
- Addiction to alcohol or drugs.
- Infection.
- There is a defect in the structure of the urinary tract without surgery to correct it.
Post-kidney transplant advice
It should be noted that a kidney transplant is one of the methods of treating kidney failure, and there are many steps and advice that the kidney recipient must follow to maintain his health and the safety of the new kidney. Below is a statement of some of the most prominent of them:
- Adherence to the diet: Although performing a kidney transplant gives the patient greater freedom to eat, a diet containing small amounts of salt and fat must be maintained in the event of high blood pressure, and attention must be paid to blood sugar levels in the event of diabetes.
- Doing exercise: Exercise helps improve heart and lung health, prevent weight gain, and improve mood.
- Adherence to immunosuppressive medications: (In English: Immunosuppressants) The patient must adhere to taking his immunosuppressive medications, as despite their side effects, they protect against the risk of the body rejecting the new organ as a result of the immune reaction.
- Pay attention to mental health: The recipient of the new kidney may suffer from many psychological changes, such as anxiety or depression as a result of immunosuppressive medications, or feelings of anxiety about the new lifestyle, or guilt, or as a result of the psychological changes he notices in those around him.