We usually hear about tooth decay, but have you ever heard of ear decay?? The ear consists of three parts: the inner, outer, and middle ear. Ear decay occurs when the temporal bones behind the middle ear dissolve.
Keratoma...the most dangerous type of caries
Keratoma is a chronic and serious infection that affects the middle ear. It consists of skin cells that grow in a place other than their normal place and begin to appear as a small cyst from the eardrum in the ear, which is located in the middle ear for several reasons. This small sac has cells inside it that grow and enlarge with time in a way that resembles the one in which the tumor grows. It then spreads to the rest of the ear, especially to the temporal bones
Keratoma is characterized by the following:
Slow-growing, it grows over many years and may cause complications after many years of illness, 5-20 years
The nature of keratoma is characterized by its ability to dissolve surrounding tissue and bone by secreting specific enzymes
It is considered an inflammatory mass filled with germs and does not reach or respond to antibiotics. It is considered a non-contagious disease and usually begins at a young age
In some cases, both ears are affected
The prevalence of inflammation in children is higher than in adults due to fragility of the temporal bones in children, but in adults, the hardening of the temporal bones reduces the spread of inflammation.
Read also:Causes of sudden nosebleedsthe reasons :
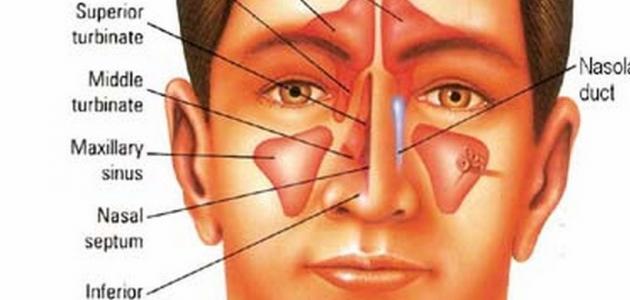
The main cause is a defect in the Eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the nose and balances the atmospheric pressure between the outside and inside the ear. When the tube closes, this causes negative pressure in the middle ear. Therefore, part of the eardrum will withdraw inward in the form of a cyst, and as the canal remains blocked, this formed cyst cysts and grows, forming a mass called keratoma.
Symptoms of cratorma
Slight dizziness and dizziness
Chronic pus is characterized by being purulent, yellowish, and having an unpleasant odor due to the associated inflammation and the type of bacteria. This inflammation does not respond to antibiotics, no matter how strong they are.
A decrease in the ability to hear due to the size of the keratoma and the occurrence of necrosis of the ossicles and the inner ear
Complications
Swelling and abscess formation behind the ear
Chronic ear piercing.
The infection spreads to the face and neck, and pus collects within the membranes of the neck and face.
Cerebral meningitis
Accumulation of inflammatory pus and pus on the cerebral membrane
Dizziness and dizziness due to injury to the semicircular canals, which are responsible for balance in the inner ear.
Vestibulitis
Read also:Causes of sudden nosebleedsParalysis of the seventh facial nerve
treatment
The only treatment for these cases is surgical intervention only under general anesthesia, through which the temporal bones are cleaned, and there is no role for conservative treatment. This operation usually gives a high success rate, but it requires high surgical skill and experience and is not for amateurs. It is preferable to perform it in early time.