Causes of polycystic ovary syndrome and risk factors for developing it
Although there is no specific and clear cause for polycystic ovary syndrome, ovarian cysts, ovarian cysts, polycystic ovary disease, polycystic ovary syndrome, Stein-Leventhal syndrome, polyfollicular ovary syndrome, or polycystic ovary syndrome (in English: Polycystic ovary syndrome). (abbreviated PCOS), but experts believe that there are several factors that play a role in its infection, such as genetic factors. Women often discover that they have the syndrome when they are in their twenties or thirties, when they face problems related to pregnancy, but this problem may occur at any age. After puberty, it affects everyone, regardless of race, but the risk of infection increases if the female suffers from obesity, or if one of the family members, such as a mother, sister, aunt, or great-aunt, suffers from multiple ovary syndrome. Bags.
Insulin resistance
It is believed that insulin resistance may be a major and important factor in the development of polycystic ovary syndrome, and what happens in insulin resistance is a decrease in the body’s ability to respond to the effect of the hormone insulin, which is secreted from the pancreas, which is responsible for helping to transport glucose. It is transported into the body's cells for use in producing energy.
Read also:The difference between period pain and pregnancy painWhen insulin resistance occurs, the body tries to compensate by producing more insulin and secreting it into the blood, causing hyperinsulinemia in the body, which prompts the ovaries to increase the production of the hormone androgen, which in turn leads to the appearance of symptoms associated with polycystic ovary syndrome. High testosterone also affects the production and development of follicles and prevents the natural ovulation process. Insulin resistance may cause weight gain, which in turn makes symptoms worse, because obesity is linked to the fat present in the body, which causes the production of more insulin. In general, Most women with polycystic ovary syndrome have some degree of insulin resistance, excess weight, and abnormal blood fat readings. However, insulin resistance tends to be more pronounced in women who are obese and anovulatory.
In addition to the above, high values of the hormone testosterone cause problems with the menstrual cycle, reduce fertility, and cause excessive growth of body hair and thinning of hair on the head. What also increases the possibility of developing insulin resistance is the following: poor eating habits, lack of physical activity, in addition to a medical history in The family suffers from diabetes, usually type 2. Over time, insulin resistance may cause type 2 diabetes. Based on the above, weight loss is usually associated with an improvement in symptoms, regardless of the underlying cause of insulin resistance.
Read also:What is the treatment for ovarian cyst?
hormonal disorders
Many women with polycystic ovary syndrome suffer from hormonal disorders, which, as previously mentioned, include an increase in testosterone. It is worth noting that although this hormone is known to be a male hormone, it is naturally secreted in the female body, but in a small percentage, and other hormonal disorders include What follows:
- An increase in luteinizing hormone, or luteinizing hormone (LH), which is one of the hormones secreted by the pituitary gland located at the base of the brain. It helps stimulate ovulation, and it also works alongside insulin to enhance the production of Testosterone, but a significant increase in the level of luteinizing hormone has unnatural effects on the ovaries, as high levels of it have actually been found in some women with polycystic ovary syndrome, and its high level with high insulin levels increases the possibility of the ovaries producing more testosterone.
- Low levels of sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), which is a protein in the blood that binds to testosterone and reduces its effect.
- An increase in the level of the hormone prolactin occurs only in some infected women. This hormone helps stimulate the mammary glands’ production of milk during pregnancy.
The underlying cause of these hormonal disorders in women remains unknown specifically, but the problem may be from the ovary itself, or from other glands responsible for producing these hormones, or from the brain in the part responsible for controlling the production of these hormones, and these hormonal disorders may result from The aforementioned insulin resistance. Some evidence has indicated the possibility of problems with the enzymes responsible for producing male hormones causing polycystic ovary syndrome. These hormones control the development of male characteristics such as male pattern baldness, and the female body produces them naturally in small amounts. Specifically, these hormones are secreted from the ovaries and glands. The adrenal gland, and its increase causes various problems such as acne, excess hair, and other symptoms associated with polycystic ovary syndrome, as mentioned previously.
Read also:Ways to speed up menstruation
Simple inflammation
The term low-grade inflammation is used to describe the production of white blood cells responsible for attacking infections. Research has shown that women with polycystic ovary syndrome have a type of mild inflammation that stimulates the ovaries to produce androgens. Which may lead to cardiovascular problems.
genetic factor
Although polycystic ovary syndrome is not usually inherited from parents, it may be inherited in some families, as some researchers indicate that certain genes cause polycystic ovary syndrome, and the incidence increases if a close family member is afflicted with the syndrome. Like a mother or sister.
Facts about polycystic ovary syndrome
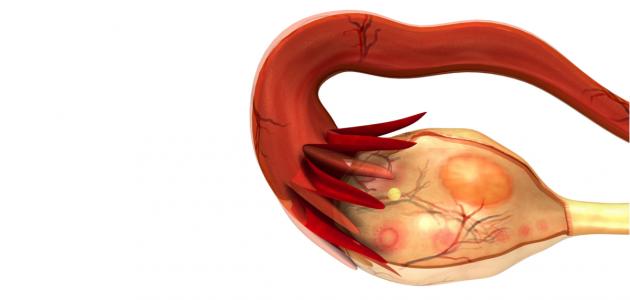
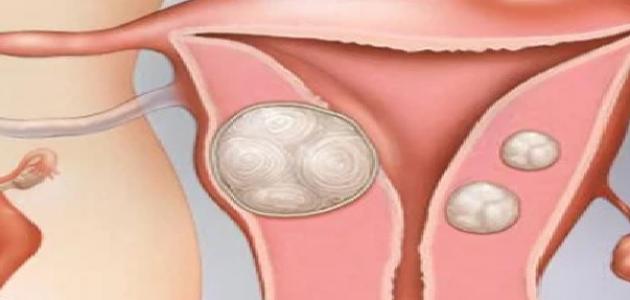
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a health problem resulting from a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. The female has two ovaries in her reproductive system, which store and release eggs and produce sex hormones. Every month, one of these ovaries releases an egg ready for fertilization, and this egg goes through stages before its release. It grows inside a small fluid-filled sac called a follicle, and usually more than one egg begins to grow, but only one egg matures fully and is released later. What happens in polycystic ovary syndrome is that 12 or more follicles begin to grow without any developing. These follicles develop into cysts that remain on the ovaries, containing immature eggs. It is worth noting that it is possible for the patient to have several cysts on the ovary without suffering from polycystic ovary syndrome, and vice versa. The syndrome may develop in some people without the presence of a polycystic ovary syndrome. Any cyst on the ovaries.
Prevention of polycystic ovary syndrome
Although it is not possible to prevent polycystic ovary syndrome, early diagnosis may help prevent various complications, such as infertility, diabetes, and other long-term problems, in addition to controlling various symptoms, through adherence to good nutrition and weight control.
Polycystic ovaries treatment
There are many different treatments for polycystic ovary syndrome, which are chosen depending on the symptoms that the patient suffers from, other health problems, and her desire to become pregnant. For example, if the patient wants to become pregnant and have children, her treatment may depend on fertility medications that are taken orally or by injection, but if If the patient does not want to become pregnant, birth control pills may be used to prevent pregnancy in addition to regulating the menstrual cycle. The menstrual cycle is usually regulated when using the hormone progesterone. Considering the non-hormonal treatment options, there is a medicine used It is usually possible for diabetics to resort to it even if the patient does not have diabetes, as this medication may help restore the level of fertility to normal and reduce the patient’s weight. With regard to other symptoms such as unwanted hair growth and acne, birth control pills may help. Treating it, but it must be noted that with regard to these and other symptoms such as obesity and diabetes, it is necessary to consult a specialist to take the necessary and available steps to deal with and control them.