Symptoms of diabetic retinopathy
The sense of sight is not clearly affected unless the condition of diabetic retinopathy progresses, and this condition, like other medical conditions, may not be accompanied by any pain or symptoms in the early stages of the disease, and its initial signs may be detected through Eye pictures taken during examinations to detect eye disorders related to diabetes. In fact, the appearance of symptoms often means that the condition of diabetic retinopathy is advanced, and in some cases sudden blindness is the only apparent symptom. Other signs and symptoms of retinopathy include the following:
- Blurred eyes.
- Poor color vision.
- Eye floaters (in English: Floaters); Or the appearance of transparent, discolored spots or dark threads in the field of vision, which may prevent the ability to see.
- Poor night vision.
- Sudden complete loss of vision.
- Visual acuity fluctuates.
- The appearance of dark or empty areas in the field of vision.
- Seeing colors are dull or pale.
- Pain in the eye.
- Double vision (in English: Diplopia).
- Eyestrain.
- headache;
- Having difficulty reading.
- Feeling of pressure in the eye.
Read also:Report on diabetes
Symptoms that require seeing a doctor
Treating and controlling diabetes is the best way to avoid vision loss, including regular eye examinations, even if the affected person thinks his vision is fine. It should also be noted that pregnancy makes diabetic retinopathy worse, so the doctor may request that the woman undergo more eye examinations throughout the course of her pregnancy. During her pregnancy, in general, a diabetic person must consult a doctor as soon as changes in vision occur, such as vision becoming blurry or blurry, or if any of the following symptoms appear, noting that they do not exclusively mean the presence of diabetic retinopathy, but require attention, follow-up, and examination. :
- Eye redness or pain.
- The appearance of eye floaters.
- Gradually weakening of vision.
- Sudden blindness.
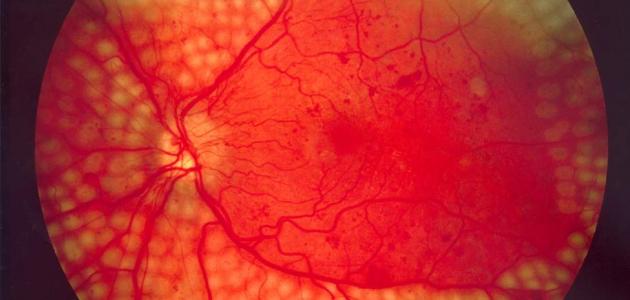
Information about diabetic retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy, also known as diabetic retinopathy or diabetic retinopathy, is a complication of diabetes resulting from damage to the blood vessels that supply the light-sensitive retinal tissue at the back of the eye. Diabetic retina is often both eyes, and both types of diabetes may be associated with it. The first or second, the longer the duration of diabetes and the less control the blood sugar level; The possibility of developing its complications, including retinopathy, has increased. Therefore, undergoing eye examinations and adhering to their schedule is the only solution to avoid developing diabetic retinopathy, so that the diabetic person undergoes a comprehensive dilated eye exam (in English: Comprehensive dilated eye exam) at least once a year to avoid the development of the disease. Diabetic retinopathy and the complications that may result from it, such as vision loss and blindness. This is because the early stages of retinopathy are not accompanied by symptoms. Therefore, detecting the disease early and controlling diabetes by taking medications regularly and following a balanced diet and exercising help preserve vision and delay or avoid blindness completely.
Read also:what are the different types of Diabetes