Renault phenomenon
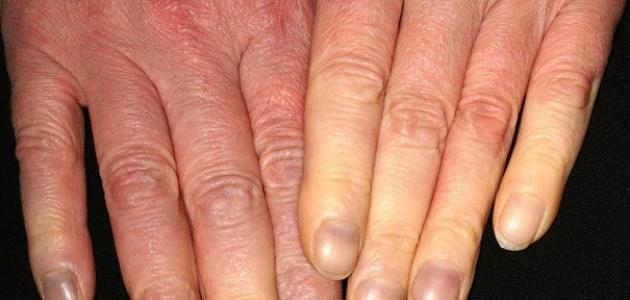
Raynaud's phenomenon, or what is known as Raynaud's disease, is defined as a disorder that affects blood vessels, which leads to a decrease in the amount of blood reaching the extremities, often in the fingers or toes, and sometimes the blood vessels in the The nose, lips, or the external parts of the ear, which leads to a change in the color of the affected part, as it may change its color to white or blue, and it may become cold and numb, and this disorder is characterized by the occurrence of episodes of contractions of the vessels, called seizures Vasospasm attacks, which cause repeated contractions in the small blood vessels in the fingers and toes, in response to low temperatures, or as a result of exposure to nervous and emotional situations, and it is worth noting that approximately 5% of people in the world suffer from Raynaud's phenomenon, but it is more common among women and girls, especially in the age group of less than 25 years.
Types of Raynaud phenomenon
Raynaud's disease is divided, according to the cause of its occurrence, into two main types, namely: primary Raynaud's Phenomenon: and secondary Raynaud's phenomenon (in English: Secondary Raynaud's Phenomenon). Diseases or problems that may cause Raynaud's disease, and it is worth noting that about 60-90% of cases with primary Raynaud's phenomenon are women between the ages of 15-40 years, and as for secondary Raynaud's phenomenon, it is less common than the first type, and often They are the result of an underlying disease or health problem, and secondary Raynaud's phenomenon is common among people who suffer from connective tissue diseases, as some of these diseases cause thickening of small blood vessels, and make them more susceptible to contraction, which leads to This leads to a decrease in the amount of blood reaching the fingers or toes, and it should be noted that about 85-95% of patients with limited scleroderma develop Raynaud's disease, and about a third of those with lupus The comprehensive water (in English: Systemic lupus erythematosus) suffer from Raynaud's disease, in addition to that, this phenomenon may affect people who suffer from other connective tissue diseases; These include Sjögren's syndrome, dermatomyositis, and polymyositis.
Read also:Seasonal influenza vaccinationSymptoms of Raynaud's phenomenon
A person with Raynaud's disease may show some signs and symptoms, and these symptoms depend on the severity of the vascular spasm attacks. When a vascular spasm attack occurs, the sensory nerves become irritated due to lack of oxygen. Treatment may lead to gangrene (in English: Gangrene) in some rare cases, and symptoms of Raynaud's phenomenon include the following:
- Cold fingers or toes.
- A change in skin color in response to cold or stress, as the skin becomes white and then gradually turns blue.
- Feeling of numbness, tingling or stinging pain, when the temperature rises or the stress is gone, then the skin turns dark red, the fingers may swell, and the person feels itchy.
Diagnosis of Raynaud's phenomenon
Raynaud's disease is usually diagnosed when the doctor asks about the symptoms felt by the patient, the times of their occurrence, the frequency of their appearance, and their causes, then the doctor examines the fingers and toes of the hands, and some doctors may use a special magnifying lens; It is called a dermatoscope (in English: Dermoscope) to examine the small blood vessels that supply the fingers, and discover if they are deformed or enlarged, and in some cases the doctor may resort to requesting a blood test and other tests, when symptoms indicate secondary Raynaud's disease resulting from other health problems and autoimmune disorders.
Read also:Yeast deficiency diseaseRaynaud's disease treatment
Until now, there is no definitive treatment for Raynaud's disease, but there are some procedures that reduce exposure to vascular spasms, and they can reduce the severity of symptoms and prevent tissue damage. For simple cases of Raynaud's phenomenon, keeping the limbs warm By wearing socks and gloves, it can help greatly, but in moderate and severe cases, the doctor may resort to the following treatment methods:
pharmacological treatments
Among the medications used to relieve the symptoms of Raynaud's phenomenon, we mention the following:
- Alpha 1 blockers: (in English: Alpha-blockers), alpha receptor blockers can prevent norepinephrine from performing its function of constricting blood vessels, and examples of these drugs are: Doxazosin and Prazosin.
- Calcium channel blockers: Calcium channel blockers Dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers help dilate the small blood vessels in the fingers and toes, which helps increase blood flow to these vessels. Examples of these are: Medicines: Amlodipine (in English: Amlodipine) and nifedipine (in English: Nifedipine).
- Nitroglycerin: Topical nitroglycerin ointment can be used to relieve symptoms by improving blood flow.
Medical and surgical procedures
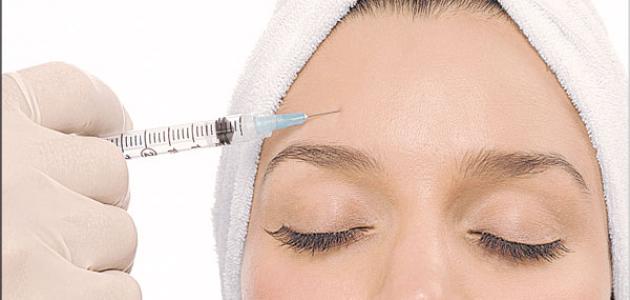
In severe cases of Raynaud's disease, it is possible to perform neurosurgery by making small incisions and stripping the affected blood vessels of nerves, in order to reduce the frequency and severity of seizures, but this procedure may not succeed in some cases, and it is also possible to use chemical injections (in English Chemical injections) to inject chemicals that prevent nerve fibers from narrowing small blood vessels. Examples of these chemicals are local anesthetics and Botox. This treatment is somewhat effective, but Its effect may wear off with time, leading to the need for repeat treatment.
Read also:How do I get rid of dizziness