Is there a sure way to diagnose rheumatism?'
Rheumatism can be diagnosed by a specialist doctor, but there is no single and certain method for diagnosis Rather, the doctor relies on a set of examinations and radiological images to be able to diagnose the condition, and the symptoms of rheumatism are similar to a group of other medical conditions, which makes diagnosis more difficult. These conditions include lupus, psoriatic arthritis, and polymyalgia rheumatica.
'How do doctors diagnose rheumatism?
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that results from antibodies attacking healthy cells in the body by mistake, causing inflammation and pain in the affected parts of the body and a group of other symptoms. The doctor needs to perform many physical and laboratory tests to diagnose the condition of rheumatism. This requires important tests to diagnose rheumatism.
The most prominent ways a doctor diagnoses rheumatism are as follows:
The doctor's evaluation of the symptoms of rheumatism and the patient's medical history
Diagnosing the condition begins with studying the symptoms that the affected person suffers from, studying the duration, frequency, and severity of the symptoms, and also their effect on the different parts that may be affected by rheumatism, in addition to reviewing the family’s medical history. But it cannot be relied upon solely because of the similarity between the symptoms of rheumatism and the symptoms of other diseases, especially in the early stages of the disease.
Read also:Joint pain
Symptoms of rheumatism that concern the doctor include:
- Feeling pain or stiffness in more than one joint.
- Feeling swelling or pain when touching more than one joint.
- Lose weight.
- fever.
- Weakness and fatigue.
Diagnosis of rheumatism through laboratory tests
Laboratory tests to diagnose rheumatism include the following:
Rheumatoid factor analysis
It is a test that measures the level of a protein (rheumatoid factor) produced by the immune system in the body Which can attack healthy tissue, leading to conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and others, andHigh levels of this factor are associated with the presence of autoimmune diseases. Including rheumatoid arthritis, so a positive test result indicates the possibility of rheumatism, not its confirmation.
It is worth noting that the rheumatoid factor test may sometimes be normal despite suffering from autoimmune diseases، It may be high in some healthy peopleTherefore, this test is not considered a confirmation of the occurrence of rheumatoid arthritis, and the affected person in this case needs to undergo further tests to confirm the disease.
Read also:Gout symptoms
analyzing Antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptides
This analysis indicates the presence of autoantibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptides Produced by the immune system When fighting foreign bodies, such as viruses and bacteria, which can also attack the joints accidentally in some cases, A positive result indicates the presence of these antibodies and is an indication of rheumatism, or the possibility of contracting it in the future, while the appearance of a negative result means not contracting the disease.
Antinuclear antibody assay
This test aims to determine the amount of proteins inside the cell nucleus called antinuclear antibodies (ANA)., which mistakenly attack natural proteins in the body, causing autoimmune diseases such as rheumatism, lupus, and others. The body naturally possesses small amounts of these antibodies, but their high levels and the presence of a large amount of them can indicate the presence of an immune disease, and the result of this is The test is either negative or positive.
However, a positive result does not necessarily indicate the presence of an immune disease; More tests must be performed to diagnose the condition; A healthy body has about 3-15% of these antibodies, and this percentage increases in people as they age, in addition to the possibility of higher levels of antibodies in the nucleus due to:
Read also:Causes of joint and knee pain- Taking some medicinal treatments.
- Exposure to viral infections.
- Cancer.
Comprehensive blood examination
A comprehensive blood test helps know the levels of different blood cells and detect anemia If it exists; Anemia is one of the common symptoms accompanying rheumatoid arthritis. Below are the results that can be obtained from this examination and the normal amounts in general for healthy people:
- White blood cells: 4.8 - 10.8 thousand white blood cells per microliter of blood.
- Red blood cells 4.7-6.1 million red blood cells per microliter of blood.
- Hemoglobin 14.0 - 18.0 g/dL.
- Hematocrit 42 - 52%.
- Platelets: 150-450 thousand platelets per microliter of blood.
Blood sedimentation rate test
This examination contributes to the diagnosis of rheumatism, but its result must be used in conjunction with other results and the patient’s medical history, given that the rate of blood sedimentation does not specifically indicate inflammation and can be affected by other factors.The sedimentation result is measured in milliliters of clear liquid (plasma) present at the top of the tube after one hour, but again it must be remembered that the result of this test is not final.
CRP test
This test aims to Check the levels of a protein that the liver produces in response to inflammation in the bodyHigh levels of the protein indicate the presence of inflammation or other pathological conditions such as autoimmune diseases, including rheumatism and lupus, so the lower the levels of this protein, the better and the lower the risk of cardiovascular disease.
A good reading is less than 10 mg/L. While if the analysis value is equal to this number or more, this may indicate the presence of significant inflammation in the body, such as autoimmune arthritis. And other diseases such as pneumonia and cancer. However, the doctor needs more tests, pictures and a physical examination to confirm the cause of the increase.
analyzing Antigens Human leukocyte HLA
This test looks for the presence of inherited human leukocyte antigens (HLA) in tissues; 60% of rheumatism cases are inheritedIf these tissues are present, the likelihood of developing rheumatoid arthritis increases, and of course the likelihood of autoimmune diseases also increases.
Diagnosis of rheumatism by radiological imaging
The doctor needs to complete the diagnosis through radiological images that help determine the severity of rheumatism, in addition to the possibility of tracking the progress of the disease over time. The required radiological images include:
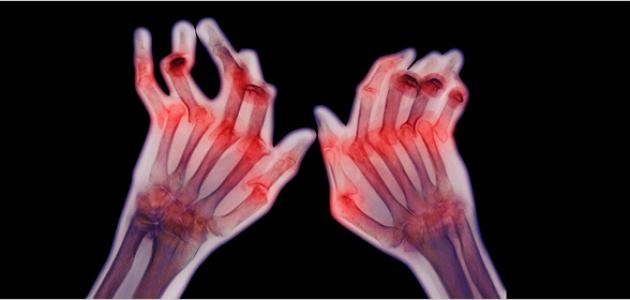
- X-ray images
Which shows damage to the joints if it exists and its amount.
- Magnetic resonance images (MRI)
Which uses magnetic resonance imaging in order to determine the degree of severity of the disease.
- Ultrasound images
Which gives more details about the condition and also helps to know the degree of severity of the disease.
'Article summary'
Rheumatism affects the joints and causes symptoms to appear in several joints at the same time, which can cause damage to the tissues of these joints and the appearance of other symptoms. Such as imbalance and severe pain, so diagnosis depends on a set of tests and analyzes that look for the presence of inflammatory factors or antibodies attacking healthy cells. Such as rheumatoid factor analysis and comprehensive blood tests, in addition to a physical and radiological examination that confirms the results of previous tests and determines the extent of the damage, if any.