The moon's rotation around itself
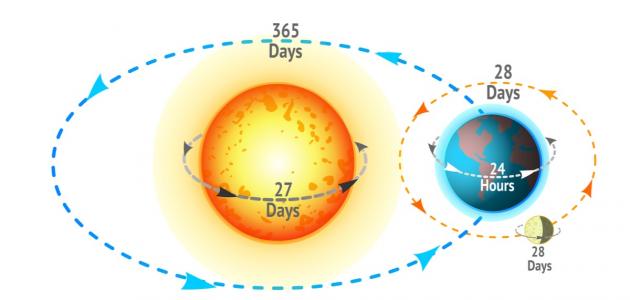
The moon rotates on its axis counterclockwise in a period of approximately 27 days, and it also revolves around the earth in relation to the stars in a period of 27.322 days, so it appears to those who look at it from the surface of the earth as if it is fixed and does not rotate, and therefore the rate of rotation of the moon around its axis is equal to the rate of its rotation around the earth, which makes the same face of the moon always facing the earth, and this is what scientists called synchronous rotation, and thus the moon has two faces, they are:
- Near moon face: It is the half of the moon facing the earth.
- far moon face It is the half of the moon that is not facing the Earth.
The Moon's rotation around its axis coincided with its orbit around the Earth
The reason for the synchronization of the moon’s rotation around itself with its orbit around the earth is due to the strong tidal forces emanating from the earth, which stabilize the moon’s direction in relation to the earth, but the degree of synchronization is not ideal for two reasons:
- The shape of the moon’s orbit around the Earth is oval rather than circular, which makes the moon’s orbital speed faster at the perigee point and slower at the aphelion point, resulting in a swinging motion between east and west of the moon inclined by 7.9 degrees throughout the month.
- The tilt of the moon's axis of rotation around itself by 7 degrees relative to its orbital plane, which produces a oscillating motion between north and south throughout the month.
far moon face
The far side of the moon differs from the near side of it, and this is represented in the absence of Maria (in English: Maria) in it, which is the large dark regions made up of cooled lava, extending over large areas of the near face of the moon facing the Earth, and instead permeates The far side of the moon has many craters of different sizes and ages. Here are the most famous space missions launched to discover the far face of the moon:
Read also:When is the sun's rays useful?- Luna 3 vehicle: (Luna 3), launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan in 1959 AD, and was the first vehicle to send back pictures of the far side of the moon, although the pictures were not clear.
- Orbital Lunar Explorer: (LRO), it was launched from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida in 2009 AD, and it took the same pictures that were taken from the Luna 3 spacecraft, but with better quality and detail, using modern imaging techniques and LRO global maps.