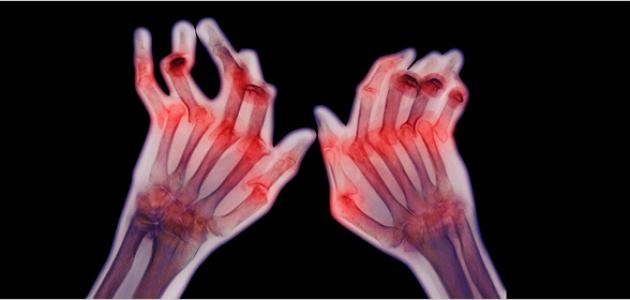
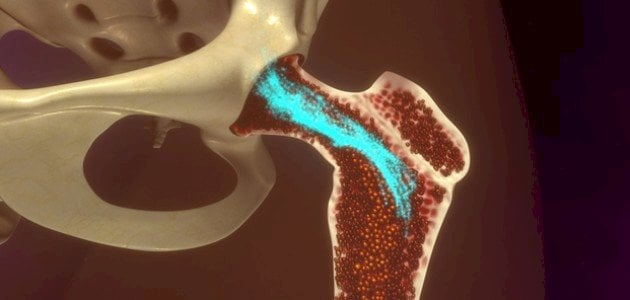
Osteitis
Osteoarthritis is considered a rare and serious condition, as it affects two people out of every ten thousand people, and it affects people of all age groups, but it is more severe and rapid in children, and it affects people with some chronic diseases such as diabetes or vascular diseases. Peripheral bacteria are more susceptible to this infection than others. In most cases, the spherical bacteria Staphylococcus aureus is the main cause of bone infection, and it may be transmitted to the bone in several ways, such as spreading through the blood from a place susceptible to infection within the body to the bones. Open fractures or surgeries, such as knee replacement, expose the bone to infection.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis
It may be difficult to distinguish between osteoarthritis and some other diseases in specific cases. This is because there are no distinct symptoms, especially in children, the elderly, or people infected with HIV. Symptoms of osteoarthritis include the following:
- Pus coming out of the skin.
- high body temperature;
- Lack of or loss of the ability to move the joint.
- nausea;
- Pain in the affected area.
- Change in walking style, or inability to bear body weight in children.
- Excessive sweating.
- Swelling of the legs, ankles, and feet.
- Swelling, redness, and warmth of the affected area.
- A general feeling of discomfort.
Read also:Symptoms of hip arthritis
Complications of osteoarthritis
There are many complications of osteoarthritis, some of which are as follows:
- Infection with septic arthritis: It is a condition in which inflammation extends to the joints adjacent to the affected bone.
- Bone death: Inflammation impedes blood circulation within the affected bone, causing it to die.
- Skin cancer: Skin surrounded by inflammation is more susceptible to squamous cell cancer.
- Poor growth in children: Especially if the growth plates become inflamed, which are the soft areas found at both ends of the bones of the arms and legs.