Brain atrophy
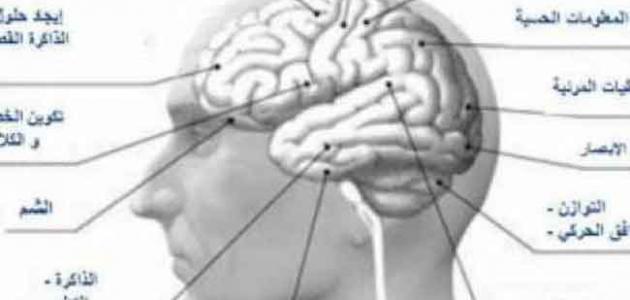
Cerebral atrophy, also known as brain atrophy, can be defined as the loss of part of the nerve cells of the brain tissue, in addition to the loss of the connections between them. In fact, this condition represents a common feature of many diseases that may affect the brain, and in general it may be The atrophy is generalized or central. Generalized atrophy is represented by the shrinkage of all parts of the brain. As for central atrophy, it is represented by the shrinkage of only a limited area of the brain, which may cause a decline in the functions controlled by this region of the brain. It should be noted that if the cerebral hemisphere is affected (in English Cerebral hemisphere (atrophy) may affect cognitive thinking and voluntary processes in the affected person. The type of atrophy occurring in the brain and the speed of its progression depends on the main cause that led to this condition.
Causes of brain atrophy
There are many different causes that may lead to brain atrophy, and the following is an explanation of some of them:
- brain attack: (In English: Stroke), this condition occurs due to an interruption of blood flow to part of the brain, which prevents the ability to deliver the sufficient amount of oxygen-rich blood that the brain needs, and thus the death of nerve cells in the affected area of the brain, which results in loss of functions. Which is controlled in this area of the brain, such as the ability to move or speak.
- Traumatic brain injuries: (In English: Traumatic brain injury), this condition may occur as a result of a fall, car accident, or any type of head blow that causes damage to the brain.
- Dementia: Dementia, in its various forms, including Alzheimer's disease, as this condition is characterized by gradual damage to brain cells and their loss of their ability to communicate with each other, leading to a significant loss of memory and the ability to think that may affect The life of the affected person. It should be noted that Alzheimer's disease is the main cause of dementia, as it is responsible for 60-80% of all cases, and it usually begins after the age of sixty.
- Cerebral Palsy: (In English: Cerebral palsy), this condition represents a movement disorder resulting from abnormal human brain growth during pregnancy, which leads to muscle motor imbalance and difficulty walking.
- Huntington's disease: (In English: Huntington's disease), it is considered one of the genetic diseases that gradually destroy nerve cells in humans, affecting the mental and physical abilities of the affected person over time. This condition usually begins in middle age, and in fact it may appear in several people. Symptoms associated with this condition, such as severe depression, and chorea, which is several involuntary movements in the body that resemble dancing.
- White matter atrophy: (in English: Leukodystrophy), this type of degeneration begins in childhood, and it is a group of rare genetic disorders that cause damage to the protective layer surrounding nerve cells called the myelin sheath, which leads to suffering from problems in memory, movement, and behavior. , vision, and hearing.
- Multiple Sclerosis: Multiple sclerosis is considered an autoimmune disease, and is represented by the immune system attacking the protective covering surrounding nerve cells, which may lead to damage to these cells over time, and thus problems with sensation, movement, and coordination. Multiple sclerosis may lead to the occurrence of several Complications such as dementia and brain atrophy. It should be noted that multiple sclerosis usually begins at puberty, and affects women more than men.
- Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: Or AIDS (in English: Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) and for short (AIDS), and its occurrence is attributed to infection with the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (in English: Human Immunodeficiency Virus), as this virus attacks the body’s immune system, and in fact this virus does not attack nerve cells directly. But it harms nerve connections through the proteins and other substances it produces, and it should be noted that toxoplasmosis (in English: Toxoplasmosis) associated with AIDS may lead to damage to the nerve cells of the brain as well.
- Brain inflammation: (English: Encephalitis), and the occurrence of this condition is attributed to several viruses. Among them are herpes simplex, which is considered the most common, the Zika virus, and the West Nile virus, as these viruses may lead to damage to the neurons in the brain.
- Neurosyphilis: Neurosyphilis: This condition affects syphilis patients who do not receive complete treatment, as it destroys the brain and the protective covering surrounding it.
Read also:What are the symptoms of brain atrophy?
Symptoms of brain atrophy
Brain atrophy may be accompanied by a number of different symptoms, including the following:
- Having nervous seizures.
- Dementia, which is characterized by memory loss, impaired executive functioning, or behavioral changes.
- Suffering from aphasia, or loss of the ability to speak, which is characterized by difficulty expressing or understanding language.
- Muscle weakness.
- Suffering from hearing loss.
Treatment of brain atrophy
In fact, there is not yet a specific or curative treatment for brain atrophy, but some treatments can be used to control some of the symptoms associated with the cause that led to this condition. Specialists advise patients with brain atrophy to monitor their blood pressure periodically, and to be sure to eat a healthy and balanced diet, in addition to To exercise; Many studies have indicated that exercising can slow down the speed of atrophy, and it is worth noting the importance of these patients remaining mentally and socially active.
Read also:Causes of right hand numbness